Amazing Guide : How Your Mobile Calls Work – From SIM to Signal Towers
Introduction
When you tap a contact to make a mobile call, it feels like magic. But behind the scenes, your phone goes through a smart process involving a tiny chip and big towers. This article will explain how your mobile call works step by step, from the little card inside your phone to the towers that carry your voice. Whether you’re talking to someone next door or across the world, this journey starts with your SIM card and ends with strong signal towers.
Table of Contents
What Does a SIM Card Do in a Mobile Call?
A SIM card, which stands for Subscriber Identity Module, is a tiny electronic chip placed inside your mobile device to connect it to the cellular network. Though tiny, it plays a big role. It holds your unique identity as a Mobile user. This chip helps your Mobile phone to know who you are, which phone number you use, and what plan or service you have. The latest advancement is eSIM (Embedded SIM) Click here to review the detailed blog on the eSIM.
When you turn on your phone, the SIM card begins its job. It connects your device to your network provider and tells the system, “This phone belongs to this user.” Without this card, your phone can’t make or receive mobile call. It also stores a few other details like your mobile settings, and sometimes, saved contacts or text messages.
How the SIM Card Gets Your Mobile Ready
As soon as you insert the SIM card into your phone and power it on, the phone checks to see if the card is valid. If it is, it tries to reach the network. This is known as registration. Think of it like entering a building and signing in at the front desk. After activating your SIM card, your phone becomes capable of communicating with other phones across the network. That’s when you can start making calls.
How a Mobile Call Begins
When you type a phone number and press the call button, your phone quickly sends a message through the network. The phone first looks for the nearest tower or signal station. It’s like yelling out to the closest person who can pass your message along. The tower catches your request and checks with the main system to see if everything is good to go.
If all is well, your call is given the green light. The system finds the person you’re calling and sends a message to their phone to ring. All of this happens within seconds, so you don’t feel any delay.
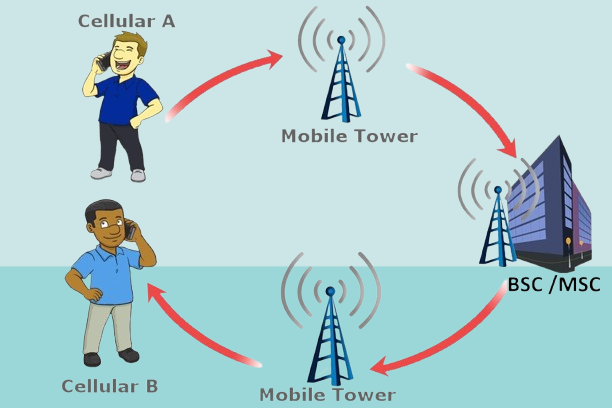
Connecting to Signal Towers
Signal towers are tall metal structures placed around cities, towns, and countryside. These towers are always ready to catch signals from phones nearby. When your phone call begins, your device sends out a signal using radio waves. These waves are caught by the nearest tower, which then passes them into the wider network.
The strength of your call depends a lot on how close you are to the tower and what might be in the way. Physical barriers like dense walls or large mountains may interfere with or reduce the strength of mobile signals. That’s why you sometimes get poor signal in basements or elevators.

What Happens Inside the Network
After your signal reaches the tower, it travels through many paths, including wires and wireless systems, to reach the destination. It goes to a central point where your call is processed. Then, it travels again, this time toward the tower closest to the person you are calling. That cell tower then transmits the signal directly to the recipient’s device.
During the call, your voice is turned into digital data, sent through this journey, and turned back into sound on the other side. This all happens so fast that it feels like you’re talking in real-time.
Moving While Talking: Tower to Tower Handover
Let’s say you’re on a call and walking or driving. You might leave the area covered by one tower and enter another. When this happens, your phone quietly switches to the next closest tower. This is called a “handover.” If done well, you won’t even notice it happened. If there’s a delay or issue, the call might drop or sound unclear.
Modern systems are designed to handle handovers smoothly. They keep checking your position and signal to ensure you stay connected as you move.
Why Calls Sometimes Drop or Sound Bad
There are many reasons a call might drop or not sound clear. One common reason is that you are far from any tower. Network congestion, such as when many users are connected at once, can also cause slowdowns or interruptions in service. This makes the system busy and your call may suffer.
Obstacles like thick walls, tunnels, or metal buildings can also weaken your signal. Weather and equipment issues can sometimes play a part too. Even though the technology is strong, these factors can cause problems.
How Technology is Making Mobile Calls Better
Phone call technology has improved a lot over the years. Today, we can make voice calls over the internet using mobile data. This means you can talk even when the regular signal is weak, as long as you have internet. In July 2023 Jazz has launched VoWiFi that can allow subscribers to call using any 3rd party Internet connection. Click here for more details
Companies are working on better towers, smarter systems, and faster ways to connect. These changes help improve voice quality, reduce call drops, and allow calls to connect faster than before.
Cellular Components
In a cellular network, several key components work together to keep your phone connected during calls. The Base Transceiver Station (BTS) is the first point of contact; it’s the tower that directly communicates with your mobile phone, sending and receiving radio signals.
These BTS units are managed by a Base Station Controller (BSC), which handles resources, call setup, and handovers between towers when you’re on the move. The BSC then connects to the Core Network, which is the central part of the system responsible for routing your call to the right destination—whether that’s another mobile phone, a landline, or even an international number. Together, the BTS, BSC & MSC, and Core Network form the backbone of mobile communication, ensuring your phone calls are seamless and uninterrupted.
Wrapping Up
The next time you make a call, remember the smart journey it takes. From the tiny SIM card in your phone to the strong towers in the distance, a lot happens in just seconds. It’s a fine example of how simple actions are backed by powerful systems. With each upgrade in technology, this process becomes smoother, faster, and more reliable. And the future promises even better connections for everyone. Click here to dive deeper into Evolution of Mobile Communication.
Frequently Asked Questions | FAQs
How does a SIM card help in making calls?
The SIM inside your phone contains unique data that lets the mobile network recognize and connect with your device. Without it, your device won’t be able to access the network or place calls.
Why do calls drop sometimes?
Calls can drop if you move too far from a signal tower, if there are barriers like thick walls, or if the network is overloaded.
Can I make a call without a signal tower nearby?
Without a tower nearby, you can’t make a regular mobile call. But if you have internet access, some phones allow calls using that instead.
How do towers know where I am?
Your phone sends a signal, and the towers nearby detect the strength and direction of that signal to figure out where you are.
What happens if I move while on a call?
Your phone switches from one tower to the next to keep the connection strong. This process is known as handoff , the process automatic and usually smooth.
Will calls become better in the future?
Yes. With newer systems being built, calls are becoming clearer and faster. In the coming years, network improvements will ensure that even far-off or rural locations experience stronger and more reliable signal coverage.